Both methods are based on the WordPress content management system (CMS) platform. However there are major differences between the two that you should understand before you make a decision. WordPress.com is a platform hosted and managed by the WordPress company, while WordPress.org is where you can download the WordPress CMS to install on your own hosted website account.
What Is WordPress.com?
If you aren’t very computer savvy, the idea of setting up a web hosting account and installing your own WordPress CMS platform may seem very daunting. If this describes you, then WordPress.com would be your ideal choice to launch your own blog. WordPress.com is a community of blog owners who are using the WordPress platform that’s hosted and managed by WordPress, the company. When you first sign up for a WordPress.com account, you’ll see two menu options – My Site and Reader. In the Reader tab, you can use the search field to search for other bloggers who’ve created blogs on WordPress.com. You can follow their blogs and return to this tab to read new posts every day. Reader is the social area of WordPress.com where you can follow the posts and conversations taking place on the WordPress blogs that you’re following.
Creating a Site Using WordPress.com
To launch your own blog, just select the My Site tab at the top of the page. If it’s your first time on the site, this page will say you don’t have any WordPress sites yet. Creating a new site using WordPress.com is as simple as selecting the Create Site button. WordPress.com offers pre-existing themes to create a business site, a personal site, and even an online store. You can select from any of these templates, or just opt to create a site with a basic template. On the next page, you’ll need to search for the main topic your blog is about, then select Continue. The next series of steps will walk you through creating a Title for your website, and the option to choose your site’s URL. You’ll have the option to purchase an actual domain name, or you can go with the free option, which is a URL that’s a subdomain of the home.blog parent domain. Editing posts in WordPress.com has the identical appearance and the same tools that are available when you self-host using WordPress.org. On the main WordPress.com dashboard, you’ll also have access to tools that you’d normally have to add and configure yourself when you use the WordPress.org self-hosting option. These tools include:
Viewing your website and post statistics.Customizing the appearance of your site.Accessing WordPress plugins, viewing blog marketing options, and choosing options to earn money from your blog.Access your WP Admin dashboard.
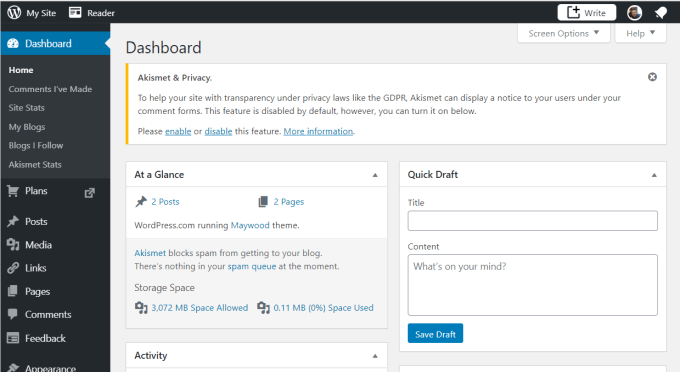
The WP Admin dashboard gives you access to the identical administrative dashboard that you have access to when you install WordPress on your own hosted website using WordPress.org. As you can see, running a WordPress site using WordPress.com is fully functional and provides you with the same sorts of features you can expect with a self-hosted WordPress blog. There are several pros and cons to consider before making the decision to go with WordPress.com. Pros:
Quick and easy blog setup.Easy to start blogging quickly.Strong social integration.Simple user interface.
Cons:
Free account is hosted as a subdomain.Less flexibility to modify your own blog themes.No access to your own hosted website files.More difficult to rank in Google search results.
What Is WordPress.org?
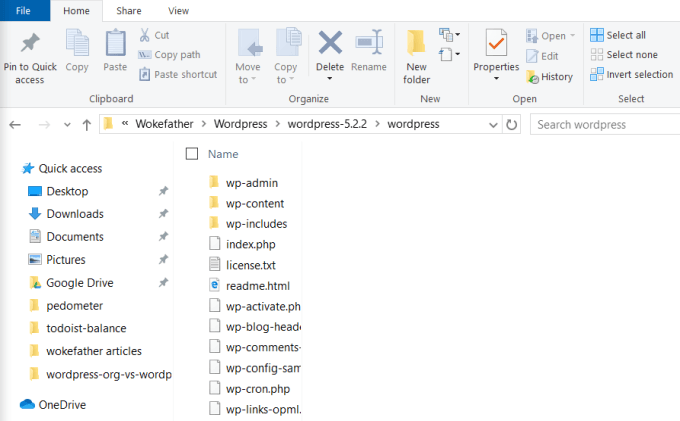
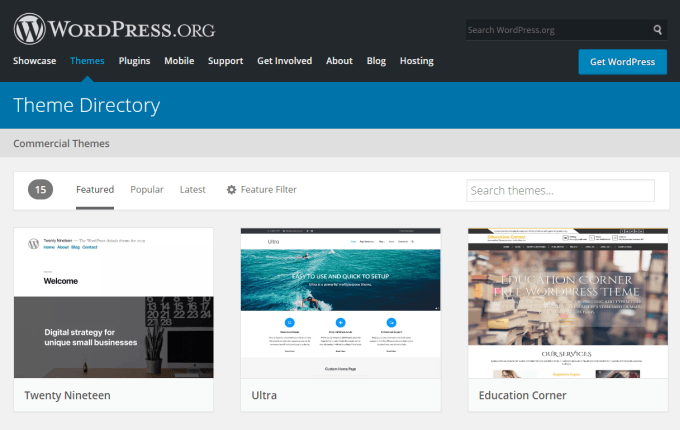
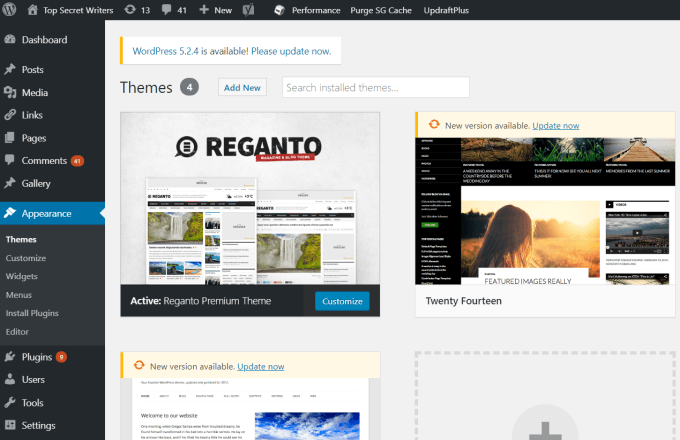
If you are able to install software on your own computer, you should be able to install WordPress onto your own hosted website. WordPress.org is where you will need to go to download the entire WordPress CMS platform that you’ll use to install WordPress on your site. When you visit the site, just select Get WordPress to get started. To download the installation files, just select the Download WordPress button and download the ZIP file that contains everything you need. Before you can install your own self-hosted WordPress platform, you’ll need to choose an affordable web hosting service where you can upload the WordPress CMS. Once you’ve signed up for a web hosting account, use the instructions from your web host to connect to your root website directory using an FTP tool like FileZilla. Unzip the WordPress ZIP file to your computer, and then upload all of the files and folders in the directory that contains wp-admin, wp-content, and wp-includes. Upload all of these files and folders to the root directory of your web hosting account. Once you’ve uploaded all of the files, you’re ready to step through the process of manually installing WordPress on your own domain. Once you’ve installed WordPress on your new web hosting domain, you’ll need to upload and install a WordPress theme to customize the style of your site. If you select the Themes link on WordPress.org, you’ll have access to hundreds of free themes to choose from. The theme that you choose and download will need to be uploaded into your hosted account inside the \wp-content\themes\ folder. Once you have WordPress installed on your site, you can access the WP Admin dashboard by adding /wp-admin/ at the end of your domain name in your browser address field. Once you access this link, you’ll see a WP Admin dashboard that’s identical to the one you would have if you’d used WordPress.com to launch your blog. Once you’ve uploaded the theme folder to your hosted website account, you can select Appearance and Themes from the WP-Admin dashboard menu to view that theme and activate it. Once you’ve set up WordPress on your own hosted domain, creating new posts for your site is identical to how you would add posts using WordPress.org. The interface looks identical, but you have access to far more customization features and plugins than if you’re only using WordPress.org. As you can see, mostly everything appears the same whether you use WordPress.com or WordPress.org. However, there are several advantages to using WordPress.org over WordPress.com. Pros:
Full access to customize any aspect of the WordPress theme that you want.No cost, regardless of how much traffic your site gets.Image storage is only limited by your web hosting storage limits.You can customize how Google search crawls your website.Easier to get listed in Google search results.
Cons:
Requires slightly higher level of computer knowledge.You’re responsible for maintaining your WordPress installation and keeping it updated.If your site gets hacked, you’re responsible for recovering it.
Either WordPress.com or WordPress.com are valid methods of launching your own WordPress site. The one you choose just depends on your level of expertise when it comes to managing a self-hosted website. WordPress.org provides people without technical skills with the ability to launch a blog if they want to.